Did you know that thousands of websites around the world are built with Microsoft Power Apps? This highlights the growing popularity of Power Apps as a low-code development platform.
Thus, if you are seeking to streamline app-building for your business, being familiar with the ins and outs of this system is crucial. Let’s explore more about Power Apps, everything from its core functionalities to its benefits, and beyond.
What are Power Apps?
Power Apps is a suite of apps, services, and connectors, along with a data platform provided by Microsoft, that offers a rapid development environment for building custom apps.
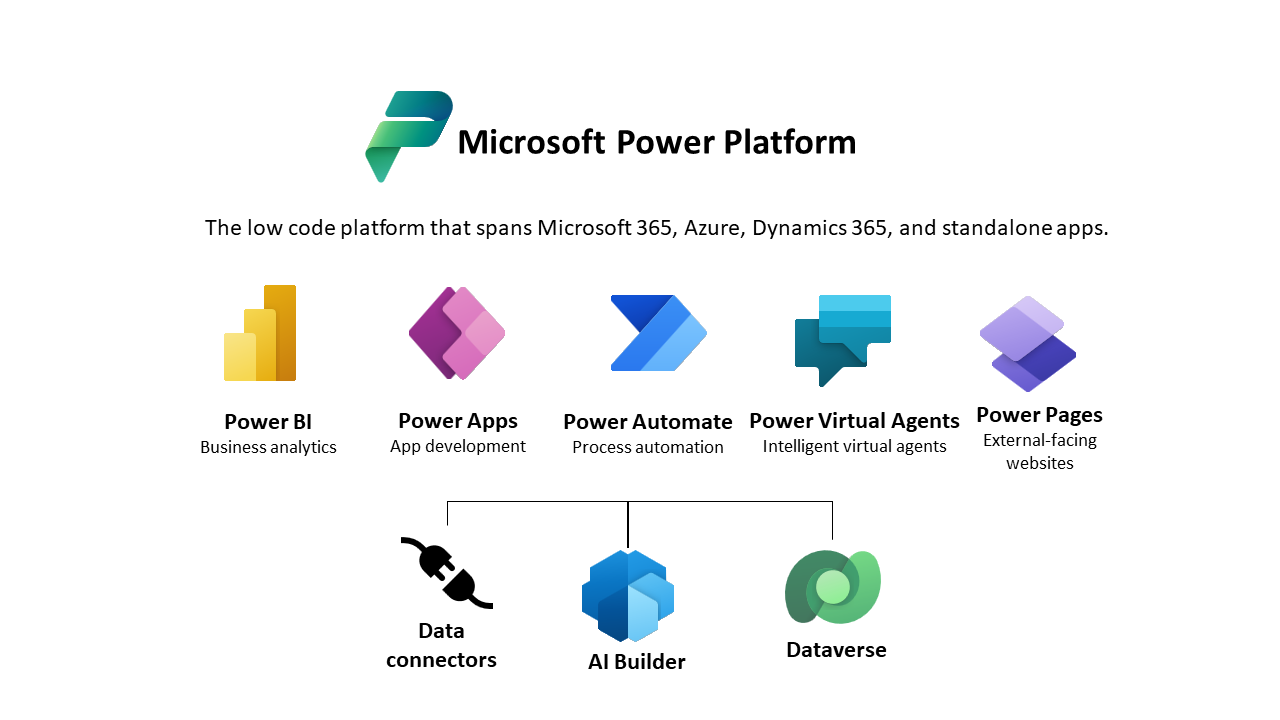
It enables you to create applications that connect to data stored in various online and on-premises sources, such as SharePoint, Microsoft 365, and SQL Server, without needing programming knowledge.
These apps are responsive and can run seamlessly across devices, empowering users to develop feature-rich, custom business applications efficiently and with minimal coding.
What are Power Apps used for?
Besides allowing the development of custom apps, the power apps have multiple other functions, which include:

- Automation: Power apps can automate routine and complex business processes like approval workflows, reporting, data entry, and more. This reduces manual efforts and minimizes errors, while simultaneously speeding up the operations.
- Mobile-compatible apps: The programs created by power apps are highly responsive as they work seamlessly across mobile devices and web browsers. This enables the workforce to access critical business information and perform tasks on the go.
- Custom forms and interfaces: It offers the ability to create custom forms and interfaces that can be connected to a data source for collecting, displaying, and modifying data. This is particularly useful for creating tailored experiences in customer engagement, employee feedback, and other interactive scenarios.
Who can use Power Apps?
The flexibility of power apps makes them suitable for various types of users, including:
- Business users: Often referred to as “citizen developers,” business users can use Power Apps to solve business problems with custom applications. They can automate processes, create forms, and develop solutions that integrate with Microsoft 365, Dynamics 365, and other services without writing code.
- Professional developers: Developers can extend app capabilities with Azure Functions, build custom connectors, and integrate with external data sources. They can also use Power Apps to rapidly prototype and develop applications, saving time on setup and basic functionalities.
- IT professionals: IT departments can use Power Apps to manage data and app security, ensuring that applications comply with corporate governance and data protection standards. Additionally, Power Apps also help them manage and monitor app usage and performance across their organization.
- Educational institutions: Teachers and students can use Power Apps for educational purposes, such as creating custom apps for administrative tasks, education tracking, or interactive learning experiences. It’s also a practical tool for teaching basic programming concepts and data management.
- Healthcare providers: Healthcare organizations can use Power Apps to create custom solutions for patient management, appointment scheduling, feedback collection, and more. This not only enhances the quality of patient care, but also aids in optimizing operational efficiency.
What types of apps can be created with Power Apps?
You can create three primary types of applications with Power Apps, each serving different purposes and suited to different development approaches:
1. Canvas apps
These apps offer a high degree of customization and flexibility, enabling you to build a user interface tailored to your exact specifications. Utilizing a drag-and-drop interface for design, Canvas Apps helps you integrate with a wide array of data sources and services.

Moreover, they support offline capabilities and allow for extensive customization through Excel-like expressions and native AI tools.
2. Model-driven apps
Model-driven apps start with your data model and use it to automatically generate a user interface that’s responsive and can adapt to various device sizes.

They are built on top of Microsoft Dataverse and focus on defining business logic and data models first, which then drives the app’s design.
These apps are highly integrated with Microsoft’s ecosystem, including Dynamics 365, making them a good choice for enterprises embedded in Microsoft’s platform.
3. Power Pages (formerly Power Apps Portals)
This type offers a way to create external-facing websites that allow users from outside your organization to interact with data in Dataverse. Power Pages are designed to share data with external customers, partners, or the general public via a secure web portal.
These portals can use data securely from Dataverse, ensuring that external users can present and interact with internal data safely.
Moreover, they support a wide range of customization and functionality, including authentication, form and view customization, and the ability to use web development techniques for a fully tailored web presence.
Benefits of Power Apps
Let’s enlist a few exceptional benefits of using Microsoft Power Apps:
1. Reduced IT costs
Traditionally, a business relies on either internal IT teams or external specialists to develop custom business applications.
The former may incur significant expenses and strain internal resources if in-house personnel have to divert attention from other crucial tasks. Similarly, depending on external contractors carries the risk of additional costs if any modifications are required in the app.
Power Apps, in such a situation, offers a transformative solution allowing you to craft tailored apps even if you lack basic know-how of programming. This saves a lot of your budget that was otherwise being spent on external developers.
2. Quick app development
The process of developing an app from scratch is quite time-consuming as it goes through different stages like coding, alpha and beta testing, and many others. Microsoft Power Apps reduce this time by creating apps quickly.

Moreover, it’s easier to modify the app by revisiting the settings in just a few clicks. The drag-and-drop capabilities of the system further simplify this task. There are fewer chances of making errors as Power Apps integrate a pre-written code.
3. AI functions
Power Apps comes with an AI builder that can incorporate different features in your app, like language detection, business card reader, and more.
It offers ready-made AI models for common tasks and guides users through creating custom models. AI Builder also helps develop smart apps that analyze data, automate tasks, and make predictions. It’s secure, and flexible, and ensures compliance with regulations, empowering your business to innovate and stay ahead.
4. Data visualization and analytics
Power Apps enables you to visualize data through interactive charts, graphs, and dashboards. The system can gather information from various sources like databases, spreadsheets, and cloud services to present it in a visually appealing format.

This way, you can gain valuable insights into your business operations and make data-driven decisions more effectively. Furthermore, the interactive nature of these visualizations facilitates exploration. This means you can go down into specific data points or dynamically filter information based on your requirements.
5. Customization
The platform provides an extensive array of customization options, ranging from templates and layouts to controls and functionalities. With this versatility, you can create highly personalized and user-friendly interfaces that align closely with your organizational workflows and processes.
Moreover, the platform’s flexibility extends beyond surface-level customization, allowing you to integrate custom logic, workflows, and data sources seamlessly.
Power Apps integration
While Power Apps integrate multiple third-party services, let’s have a look at some major ones:
- Office 365: Through this integration, Power Apps utilizes functionalities of different apps like Outlook, Excel, and Teams, to help enhance collaboration and productivity within your organization.
- SharePoint: This integration allows Power Apps to access and manipulate data stored in SharePoint lists and libraries, making it easier to create apps that interact with SharePoint content.
- Dynamics 365: Integration with Dynamics 365 enables Power Apps to interact with customer relationship management (CRM) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) data, allowing your company to build custom apps that extend the functionality of Dynamics 365.
- Azure: Azure services provide Power Apps with access to advanced cloud computing capabilities, such as AI and machine learning, data storage, and serverless computing, enabling the development of powerful applications.
- Google Drive, Dropbox, and Box: You can use Power Apps to easily access and manipulate files stored in these cloud storage platforms. This will make it easier for you to manage documents and collaborate within applications.
- Slack: Via Slack, Power Apps can send notifications, messages, and updates to Slack channels and users, making it easier to communicate and collaborate within teams.
Some other third-party integrations of Power Apps include:
- Resco
- Mailchimp
- Twilio
- ServiceNow
- Trello
- Salesforce
Power Apps use cases
The capabilities of Power Apps can be evaluated by some use cases, as we have discussed below:
- Field workers: Power Apps can be used to create applications that allow field workers to log repair work or inspection results directly from their mobile devices, streamlining data collection and reporting.
- Document automation: Power Apps can automate the creation of standard documents, such as contracts, using predefined templates that pull data from various sources. It’s particularly prevalent in legal, procurement, and human resources departments.
- Appraisal systems: HR departments could use Power Apps to build customized appraisal systems that allow for various forms of feedback and evaluations from multiple users.
- Asset tracking: IT departments can track physical and software assets through applications built with Power Apps, helping manage inventories and license renewals efficiently.
- Marketing automation: Marketing teams may develop tools within Power Apps to automate follow-up actions based on client interactions, enhancing customer engagement and response time.
How to build an app with Power Apps
The app-building process with Power Apps consists of various phases. For your ease, we’ve discussed each of them below:
1. Planning
In this step, you have to identify certain factors to put the foundation of the application. This includes a thorough understanding of the problem that your app will solve along with its targeted users. Similarly, it’s crucial to outline the objectives and goals of the app.
The planning phase also involves getting familiar with the business process and data you’ll need to organize, access, and store.
2. Creating and setting up data
Next up, your task is to create a new app by signing in to Power Apps Studio through the web or desktop client.
Select between a canvas app (starting from a blank canvas and designing your app by dragging and dropping elements) or a model-driven app (based on your data model and processes).
Then, using the Data panel, you can search for and add connections to your data sources. You might need to authenticate to these sources depending on what they are.
3. Designing phase
The steps that you need to take in this step depend on the type of app you have chosen:
- Canvas app: If you’re building a canvas app, you’ll design your app in a free-form canvas. Use the insert pane to add controls like text boxes, labels, and buttons. Bind controls to your data source to display and interact with the data.
- Model-driven app: For model-driven apps, your app’s design is determined largely by the structure of your data. You’ll have to configure forms, views, and charts to present the data.
4. Adding logic and automation
Similar to Excel, Power Apps uses formulas to control the behavior of app components. This can be used for navigation, data manipulation, and logic.
Integrate with Power Automate: For more complex workflows or actions (like sending emails or notifications), you need to integrate your app with Power Automate.
5. Previewing and testing
Use the preview function to test your app’s functionality and user experience. Make adjustments as necessary based on your findings. Once you’re satisfied with your app, publish it to make it available to your users.
Operating systems/browsers/platforms supported by Power Apps
Here’s a breakdown of OS, browsers, and platforms, supported by Power Apps for launching applications:
Operating systems:
- Windows: Windows 10 and later versions
- iOS: iPhones and iPads running iOS 12 or later
- Android: Android 7.0 (Nougat) or later
Browsers:
- Microsoft Edge
- Google Chrome
- Mozilla Firefox
- Apple Safari
Platforms:
- Web: Browsers on desktop and mobile devices.
- Mobile devices: Dedicated mobile apps for iOS and Android, providing a native app experience for users on smartphones and tablets.
- Microsoft Teams: Can be embedded within Microsoft Teams, allowing users to access and interact with apps directly within the Teams environment.
Wrapping up
Power Apps empowers anyone, regardless of coding experience, to build custom applications that streamline workflows, automate tasks, and improve data management. With rapid creation, deployment, and management features, Power Apps puts the power of app development in your hands. So, are you ready to build the app that transforms your workflow?